Contents
What is Sieve Analysis? Standards and Methods
Sieve analysis is a crucial laboratory method used to determine the particle size distribution of aggregates. This method employs a series of standard sieves to identify the distribution of different-sized aggregates. Sieve analysis plays a significant role in evaluating aggregate quality and determining gradation, which directly affects concrete performance.
Sieves have specific aperture sizes and are carefully selected according to standards such as ASTM E11-12 or ISO 3310-1. The primary goal of sieve analysis is to determine the proportion of each particle size within an aggregate sample. This analysis is critical for measuring gradation and optimizing the workability of fresh concrete mixtures.
Granulometry and Its Importance for Concrete Performance
Granulometry refers to the distribution of particle sizes in aggregates. This distribution directly impacts the durability, density, and workability of concrete mixtures.
The gradation of concrete affects its performance from the fresh mix stage to its hardened state. Ideal granulometry is achieved when coarse and fine particles are evenly distributed. This prevents segregation in concrete and ensures a dense structure. Proper gradation also helps in the cost-effective use of aggregates.
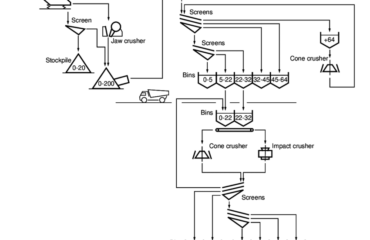
Round-Hole and Square-Hole Sieves: Which Type is Used in Which Situation?
The type of screen used in aggregate sieve analysis directly affects the accuracy of particle size separation. Older Turkish Standards allowed the use of both round-hole and square-hole sieves. However, newer specifications have standardized square-hole sieves.
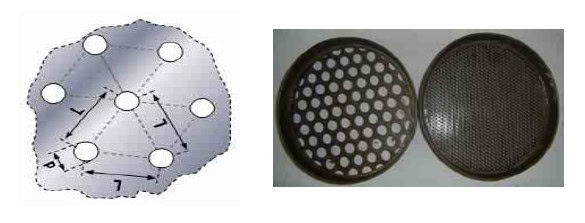
– Definition: Sieves with circular apertures, typically used for coarse-grained materials.
Round-Hole Sieves:
– Advantages:
– More durable and suitable for heavy materials.
– Commonly used for materials like railway ballast and base layers.
– Disadvantages: Less precise in determining gradation compared to square-hole sieves.
Square-Hole Sieves:
– Definition: Sieves with equally spaced square apertures.
– Advantages:
– Provide more accurate separation of aggregate sizes.
– Compliant with current Turkish Standards and yield more precise results in granulometry analysis.
– Applications: Ideal for concrete production, asphalt mixtures, and other precise gradation tests.
Impact of Round-Hole and Square-Hole Sieves on Granulometry
Natural aggregate materials often do not conform to standard granulometry values. Therefore, coarse and fine materials must be mixed in specific ratios. The correct choice of sieves plays a critical role in achieving the desired granulometry.
– Round-hole sieves offer a more durable option for separating coarse particles but provide less precise measurements in gradation tests.
– Square-hole sieves, compliant with modern standards, ensure accurate classification of aggregate sizes.
Achieving Ideal Granulometry Through Sieve Analysis
– Ideal granulometry is achieved through a particle size distribution that prevents the segregation of coarse and fine particles during the mixing, transporting, placing, and compacting of fresh concrete. This ideal distribution is determined through sieve analysis.
– Determining gradation verifies the quality and suitability of aggregates for concrete. Therefore, sieve analysis is rigorously applied in mineral processing plants. In laboratories, standard sieve sets are used to calculate the percentage of material passing through specific sizes, and the resulting gradation is checked for compliance with project-specific specifications.
Sieve analysis and granulometry play a critical role in measuring aggregate quality and concrete performance. These methods are widely used not only in concrete but also in asphalt, dam fill materials, and railway ballast. Understanding the differences between Turkish and ASTM standards facilitates working with accurate specifications. Compliance with these standards helps achieve maximum performance and cost efficiency in projects.